Microsoft Teams: Create a Governance Plan
Microsoft Teams has become essential for organizational collaboration, especially with the rise of remote work. However, the more your organization relies on Teams, the more crucial it is to manage its growth and ensure it’s used responsibly. A comprehensive governance plan for Teams will help you avoid common pitfalls, like sprawl, security risks, and unmanaged data. In this guide, we’ll walk through creating an effective governance plan, covering essential policies like naming conventions, guest access, and data retention strategies. By implementing these policies, your organization can stay organized, secure, and compliant.
Define Clear Naming Conventions
Establishing consistent naming conventions is critical for keeping Teams organized and easy to search. Without these, you can end up with multiple teams with similar or ambiguous names, making it hard to locate the right team or channel.
- Use Standard Prefixes or Suffixes: Decide on prefixes or suffixes that specify departments, locations, or project types (Example: MKT-, HR-, or Project-2024).
- Role-Based Naming: Consider naming channels based on function, such as General, Announcements, or Resources.
- Special Characters and Casing: Avoid using special characters, excessive capitalization, or other styles that might confuse users or interfere with search functionality.
Once established, apply these naming conventions consistently across teams and channels. Some organizations may even use automation (like Power Automate) to enforce these conventions and prevent accidental deviations.
Guest Access and External Collaboration Policies
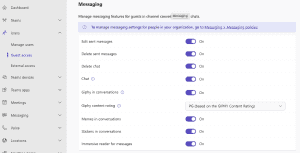
Allowing guest access can be a powerful way to collaborate with external stakeholders, but it also introduces risks. Establish policies around guest access to maintain control over who has access to sensitive information.
- Enable or Disable Guest Access: Decide whether you want to allow external guests to join Teams at all. This can be turned on or off organization-wide.
- Set Up Guest Access Approval Workflows: If guest access is allowed, consider setting up an approval workflow so that guest access must be approved by team owners or IT.
- Restrict Guest Access Permissions: Customize permissions so that guests have limited capabilities (e.g., read-only access to specific channels) while ensuring they can’t add or delete content freely.
- Review and Monitor Guest Access Regularly: Set a schedule to review guest access in teams periodically, ensuring that former clients, vendors, or other collaborators no longer have access after their engagement ends.
Channel and Team Creation Policies
Creating a policy for who can create new teams and channels prevents sprawl and duplication, helping to keep your Teams environment manageable and organized.
- Limit Team Creation Permissions: Consider restricting team creation to certain users, such as team leaders or project managers, instead of allowing everyone to create teams.
- Set Team Owners and Channel Moderators: Assign designated owners and moderators for teams and channels to ensure someone is responsible for managing membership, organizing content, and enforcing policies.
- Periodically Review Teams: Conduct regular reviews to identify inactive teams. Decide whether these teams should be archived or deleted, depending on your retention policy.
Data Retention and Archiving Strategies
Data retention is essential for compliance, especially for organizations subject to regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. It also helps keep Teams storage manageable by removing or archiving unused content.
- Define Data Retention Policies: Establish policies for how long Teams conversations, files, and channels should be retained. You can set retention policies at different levels (Example: for the entire organization, specific departments, or individual teams). We go over how to setup a Teams retention policy here.
- Implement Auto-Archiving: Configure Teams to automatically archive inactive channels or teams after a specified period. Archived teams remain accessible but are read-only, which helps control clutter without fully deleting historical information.
- Back Up Data Regularly: Use third-party backup tools or native Microsoft 365 options to ensure your Teams data is securely backed up. In the event of accidental deletion or cyber incidents, having a reliable backup can be a lifesaver.
Security and Compliance Policies
Security is a key part of any governance plan. Teams offers numerous security settings that help safeguard sensitive information and ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for all users to add an extra layer of security, especially for users accessing Teams remotely or from mobile devices. You should already be doing with conditional access policies within Microsoft Entra for your users.
- Enforce Sensitivity Labels: Apply sensitivity labels to Teams channels, marking them as confidential, internal-only, or restricted based on the information shared.
- Set Up Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies: DLP policies help prevent sensitive information from being shared inadvertently within Teams. You can configure DLP rules to monitor messages and files for keywords or patterns related to sensitive data.
- Audit and Monitor Activity: Use the Microsoft Purview, also known as the Microsoft 365 Security & Compliance Center to set up alerts and monitor unusual activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or large data transfers, within Teams.
Communication and Training
Even the most well-thought-out governance plan will fall short if users aren’t aware of it or don’t understand it. Communication and training are critical for success.
- Provide Clear Documentation: Create user-friendly documentation that explains the key elements of your Teams governance plan. Ensure it’s easily accessible through your intranet or a dedicated channel in Teams.
- Offer Regular Training: Conduct regular training sessions on Teams best practices, emphasizing how users can follow governance guidelines.
- Establish a Support Channel: Set up a dedicated support channel in Teams where users can ask questions, report issues, or get clarification on governance policies.
You can elevate your organization’s collaboration with a comprehensive Microsoft Teams governance plan. By establishing clear policies for naming conventions, guest access, team creation, and data retention, you can ensure a structured and organized Teams environment. Prioritize security and compliance by implementing robust safeguards to protect sensitive data. Train your users and regularly review your policies to foster a culture of responsible usage. With a strong governance framework in place, your organization can unlock the full potential of Microsoft Teams and drive innovation and productivity.
I hope you find this helpful!
![]()
Categories
Recent Posts
- Google Workspace: Managing Users at Scale with Google Sheets and Apps Script
- Google Workspace: Exporting Groups with Memberships
- PowerShell Basics: Find Who Disabled AD Account
- GitHub: Hosting a free Static Site (College Football Scoreboard Edition)
- PowerShell: How to Add an Alias to Every Users Mailbox and Groups in Microsoft 365